To understand this tutorial, understanding how to create & connect an IWC client is necessary, as well as an understanding of the Data & Intents API. Advanced references are used in this application to aid in references that collect.
This tutorial does not cover the framework used to create the application (AngularJS) nor the styling applied (Bootstrap). The purpose is to show the connectivity of IWC to the applications components. The code has been generalized, the actual angular application can be found here
Location Lister
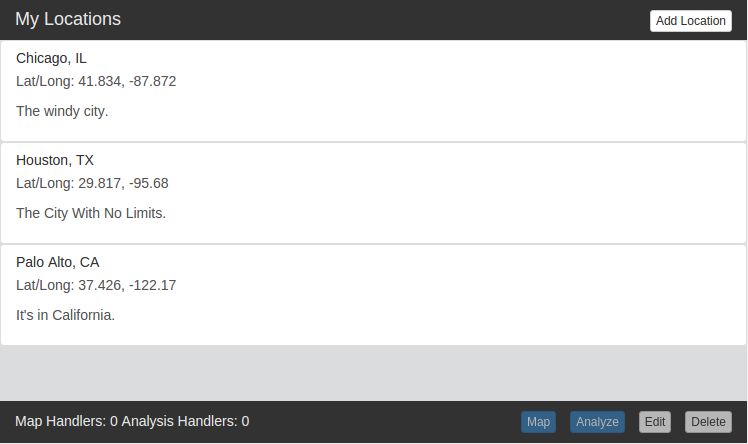
The Location Lister is one of the example apps hosted on the homepage of the IWC website. It is an application that allows users to store GPS coordinates along with any useful description data they may choose. If this application was ran on a private IWC bus (not the github hosted IWC), it could persist the users entries beyond their current session.
This application performs the following tasks:
- Create a location entry (GPS coordinate, description, and name)
- Edit a location entry
- Delete a location entry
- Dynamically list all location entries
With a mapping application open as well, this application performs the following tasks:
- Plot a location on the selected map.
With an analyzing application open as well, this application performs the following tasks:
- Send a location to be analyzed.
Dynamically List Locations
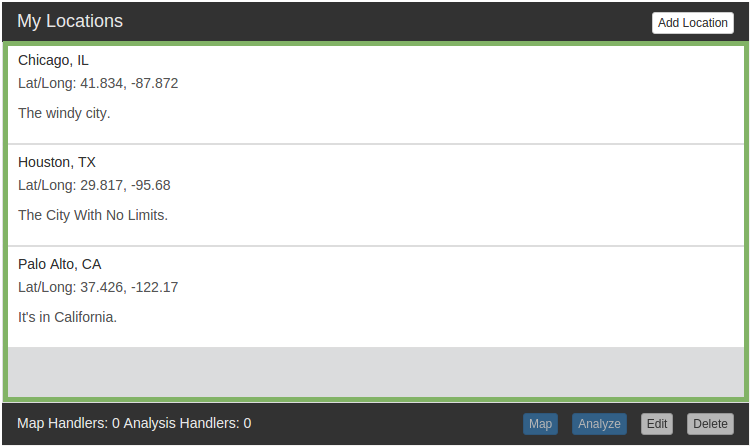 Data gathered by the /locationLister/listings reference (collection enabled)
Data gathered by the /locationLister/listings reference (collection enabled)
The Location Lister application stores its locations by storing a pairing of a reference and a value locally.
To initialize the applications set of locations, a reference is generated
to the parent resource of all the location data, /locationLister/listings,
with the advanced option collect set to true to allow this reference to
receive updates about created/destroyed locations (when registering a watch).
//=======================================
// Location List: a collection of Locations
//
// IWC References (Uses in this application):
// API: Data
// Resource: /locationLister/listings/*
// Collects: none
//=======================================
function LocationList(resource) {
this.reference = new iwc.data.Reference(resource, {
collect: true
});
this.addLocation = this.reference.addChild;
this.locations = {};
var self = this;
var handleCollection = function(collection) {
collection.forEach(function(resource) {
if (!self.locations[resource]) {
self.locations[resource] = new Location(resource);
}
});
};
var onCollectionChange = function(changes) {
handleCollection(changes.newCollection);
};
// Watch For new locations added to the collection
this.reference.watch(onCollectionChange);
// Get the initial collection
this.reference.list().then(handleCollection);
}
var locationList = new LocationList('/locationLister/listings');
Disecting the above code:
The reference generated to watch and gather the list of locations is stored as a property of the
LocationListobject,locationList.locationList.referenceadds the watch callbackonCollectionChangeto handle changes to the collection.locationList.referencegets the initial collection with the list action.When the collection of locations (resources pathed below
/locationLister/listings/in the Data API) changes, if there is a new location, aLocationis created and added tolocationList.locations.LocationListties its reference'saddChildmethod toaddLocationfor simple additions to its collection.
List Location Structure
//=======================================
// Location
//
// IWC References (Uses in this application):
// API: Data
// Resource: /locationLister/listings/<AutoGenerated ID>
// Collects: none
//=======================================
function Location(resource) {
this.reference = new iwc.data.Reference(resource);
this.resource = resource;
this.update = this.reference.set;
this.delete = this.reference.delete;
this.value = {};
var self = this;
var onChange = function(changes) {
self.value = changes.newValue;
};
this.reference.watch(onChange).then(function(val) {
self.value = val;
});
}
Disecting the above code:
* Each Location contains a reference to its location's resource.
Each
Locationwhen constructed, registers a watch callback to update itsvalueproperty whenever the resource changes.Each
Locationgets an initial state of its resource when constructed, because the watch promise resolves with the current state of the resource.Each
Locationwill clear itself should its resource be deleted. This is because thechanges.newValuethat is passed to theonChangecallback will equal undefined when the resource is deleted. Additionallychanges.deletedwill be set to true, but not utilized in this demonstration.Each
Locationties simple function names to its reference:updatecallsreference.setdeletecallsreference.delete
Create, Edit, and Delete Locations
Add Location
// Called when the "Add Location" button is pressed
// Opens popup modal, resolves with the input data.
// Autogenerates the resouce in the locationList collection.
var addListing = function(location) {
return locationModal(location).then(function(output) {
return locationList.addLocation(output.listing).catch(function(e) {
console.log(e);
});
});
};
When the Add Listing button is pressed:
* A UI modal is opened (not part of IWC) that resolves with the data that
will be stored in the new IWC Data Api resource.
- The
locationListfrom the above section uses theaddChildmethod to store this new data within thelistingsRefcollection (the exact resource path is autogenerated). This triggers the watch callback in the Dynamically List Locations section to update the list (on all open Location Lister applications) with a newLocation.
Edit Location
// Called when "Edit" is clicked.
var editLocation = function(location) {
if (location) {
locationModal(location.value).then(function(output) {
// Use the location's reference to update the resource
location.update(output.listing);
});
}
};
When a location is selected and the Edit button is pressed:
* The Loction that is currently selected is passed to the editLocation function.
The value is passed to the popup modal for editing. When resolved, the location's
updatemethod is called. (Alias to reference.set)The
Locationreceives the updated data in itsvaluebecause of its watch callback.
Delete Location
location.delete();
When a location is selected and the Delete button is pressed, the locations
delete method is called. (Alias to reference.delete)
Intent Use
The Location Lister uses 3 intent resources:
- Outgoing
/json/coord/map: Sends the path of aLocationresource for another application to map./json/coord/analyze: Sends the coordinates of aLocationfor another application to analyze.
- Incoming
/json/coord/save: Registers to receive formated coordinate data and createsLocationsto add to the list.
To simplify UI tie-ins, the Location Lister application wraps the creation of Intents API references into a class called Intent.
//=======================================
// Intent: A wrapper for invoking remote functions
// as well as tracking the number of
// matching functions.
//
//=======================================
function Intent(resource) {
// collection enabled to tie # of handlers to the UI
this.reference = new iwc.intents.Reference(resource, {
collect: true
});
this.run = this.reference.invoke;
this.register = this.reference.register;
this.handlers = [];
var self = this;
var handleCollection = function(collection) {
self.handlers = collection;
$scope.$apply();
};
var onCollectionChange = function(changes) {
handleCollection(changes.newCollection);
};
// Watch for updates the the collection
this.reference.watch(onCollectionChange);
// Get initial collection
this.reference.list().then(handleCollection);
}
An instance of Intent contains:
A reference to the specified Intents API resource.
Encapsulated logic for tracking the number of available handlers for the intent in its
handlersproperty. This is done by using the watch/list functionality as used on theLocationListerabove.Simplified method names:
runties toreference.invokefor calling the remote functionalityregisterties toreference.registerfor registering a function for remote use. ***
Outgoing Intents
Counter
 As explained above, the local class
As explained above, the local class Intent keeps track of its handlers,
so visually displaying the number of applications open to map/analyze is
done by accesing the Intent instance's handlers.length.
Invoking
 With the local class
With the local class Intent having a run method tied to reference.invoke,
invoking a map intent is done with:
js
var map = new Intent("/json/coord/map");
map.invoke("/locationLister/Listing/123")
The /json/coord/map intent is specified to receive a data api resource path
in order to allow the map to watch for changes and update the position.
If a location is mapped to the Location Mapper, then edited, the change will be
reflected on the map.
The /json/coord/analze intent is relies only on the coordinate data of the
location, so it does not accept the data api resource path rather an object
containing the location coordinates:
js
{
lat: 1,
long: 12
}
While the Location Lister does not expect any results on its intent invocations, an intent invocation will resolve with a result if the registered handling function returns a value.
Inbound Intents
The Location Lister registers to handle saving location data.
//=======================================
// Save Intent (Register for Remotes)
//=======================================
var save = new Intent("/json/coord/save");
var metaData = {
icon: "http://some.website.io/iconPath.png",
label: "Location Lister"
};
// The functionality to share. Opens the modal for saving the received location.
var saveLocation = function(location) {
if (location && location.title && location.coords) {
// Returns the new Location resource path to the invoker when finished
return addListing(location);
}
};
save.register(metaData, saveLocation);
The registration takes 2 parts:
- Meta Data: the intent is registered with an icon and label. In the event
that multiple handlers are registered for
/json/coord/savethe user will be prompted with a popup and this meta data distinguishes each handler. - Handler: the function that is ran to handle the saving.
In this application a modal is opened with the received data for the user to save, and upon saving the invoker of the intent (the application that calls invoke) the output.
The output of the saveLocation handler is the Data Api path to the
new Location that was made. This is used by the Location Analyzer
to gather information about the new Location it helped create.
